Review: Topic Modeling for Arabic Language
In this blog post, we will review recent trends in topic modeling for short text via pre-trained language models. More specifically, we will focus on modeling short text for non-Latin languages such as Arabic and Japanese. In the first part (this blog), we will describe only text modeling for Arabic language.
Our code is available on Github and for quick start try interactive demo.
Also, as bonus material, we will demonstrate how to extract topics using GPT-4
Introduction
Topic modeling is a task that makes data more interpretable by
applying probabilistic learning methods in an unsupervised way. These probabilistic models can take
advantage of statistical techniques to gather a short condensed representation of
large data to highlight hidden relations (e.g., Latent Semantic Analysis
Varieties of Arabic Langauge
According to Google, Arabic is spoken by more than 422 million people around the world. There are 30 modern types, including Modern Standard Arabic. The main three types of the Arabic language are:
Classical Arabic (CA) "ٱلْعَرَبِيَّةُ ٱلْفُصْحَىٰ". Classical Arabic is the standard form of the language that was used in the Middle ages, and the language of the holy book "Qurʾān".
Modern Standard Arabic (MSA) "الُّلغةالَعَربَّيةالحَديَثة". The MSA is the currently used language in writing and speaking formally in the Arab world. Although the MSA is different from Classical Arabic, the morphology and syntax remained unchanged.
Dialectal Arabic "لهجة". The everyday settings used language and the language of social media. Each region in the Arab world has a different dialect (ie., true mother tongue) as shown in Figure 1 below. However, in this blog, we only examine the Gulf Arabic dialect.
Social media (e.g., Twitter, Facebook, etc.) and Broadcast New platforms have served as rich sources for researchers to build dialect-specific
tools (dialect detection
Text Mining in Arabic Language
Non-MSA Arabic text is heavily based on social media, more specifically Twitter. The short text comes in varieties of Arabic targeting different populations (ie., regional dialects) as shown the figure 1. For worthwhile text processing such as topic modeling (this blog), sentiment analysis, etc., preprocessing is an essential task to filter out uninformative information (e.g., stopwords, emoji, etc.). We summarized the basic preprocessing for Arabic text mining as follows:
Stopwords Removal. high-frequency words such as conjuncts or definite articles, preventing them from appearing in topics.
Diacritics Removal and Normalization. The diacritic in the Arabic language represents short vowels (Tashkeel) which can be added to the string (بـُـومة boomah = an owl), and is similar to the accent in other Latin languages e.g., in Spanish (España es un país). However, unlike other Latin languages such as Spanish, Catalan, etc., removing the diacritics will not be a problem for formal writing such as newspapers and books for native speakers. However, it will result in word ambiguity as shown in this example:
(1) I sat on the north side of the bridge.
جلستُ "شَمال" الجسر : شَمال أي إتجاه الشمال
(2) I sat on the left side of the bridge.
جلستُ "شِمال" الجسر: شِمال أي إتجاه اليسار
In the first sentence (1) the word "شَمال" means "north" side of the bridge, while in the second sentence "شِمال" refers to the "left" direction of the bridge. Therefore, each word will be treated as a different token and thus result in different lengths. Therefore, to reduce the sparsity and complexity, the diacritics can be completely eliminated from the text.
Data
In this blog, we will use ArabGend dataset a gender based Twitter dataset
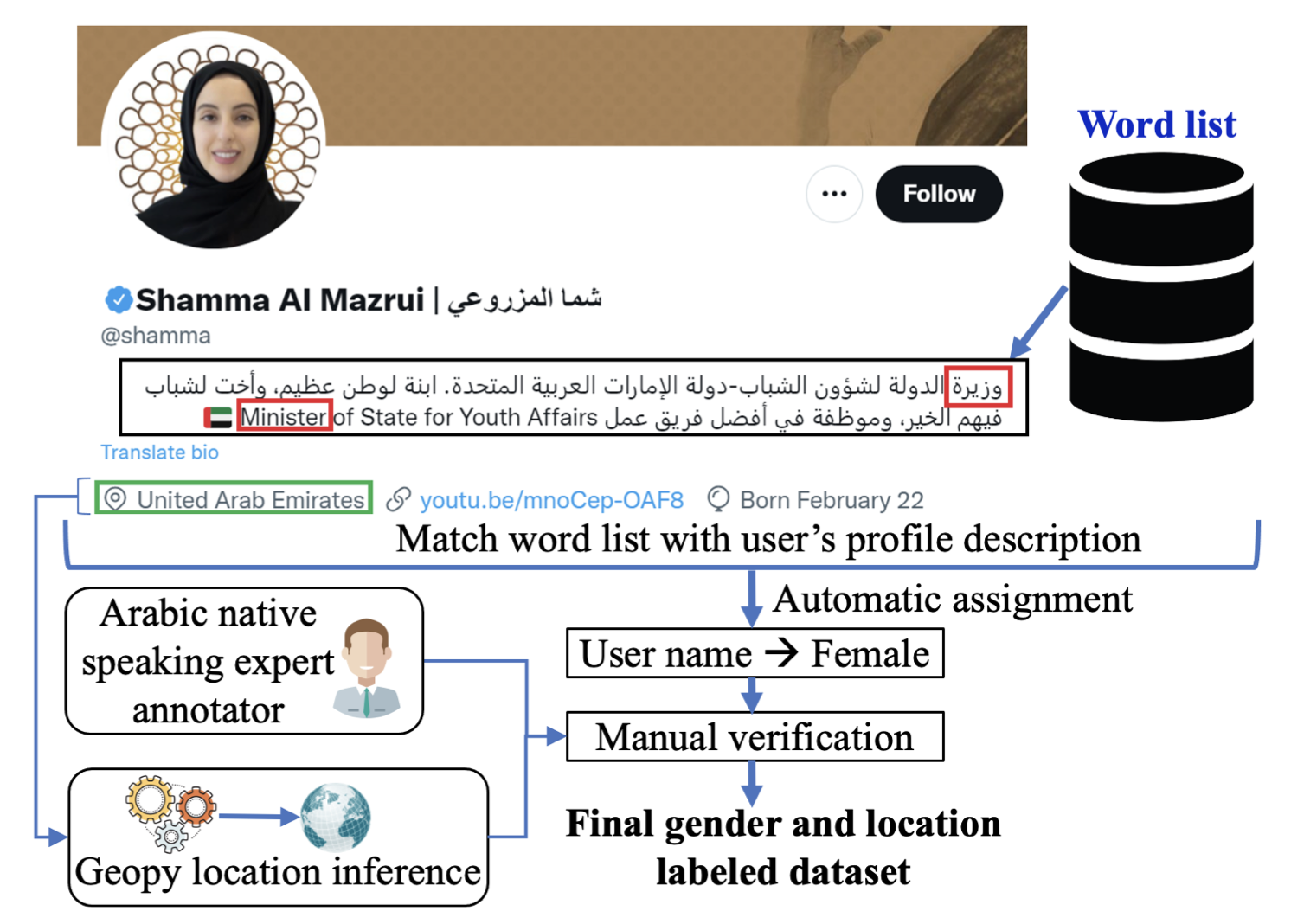
The dataset is significantly imbalanced with a ratio of 85% of tweets written by men. We will only use men's
tweets for the purpose of this blog. However, in a real scenario, we could either be collecting more women's tweets or change
the loss function to account for the imbalance (e.g., Focal loss
| Profile Name | Profile label | Location | Gender |
| Safia Alshehi | journalist (f) | Dubai | F |
| صفيه الشحي | كاتبه | دبي | م |
The results pre-processed dataset (i.e., w/o diacritics, lemmatization, w/o emoji, etc.) is (100K) 108053 line and (3M) 3175755 tokens. As shown in Table 2 below two tweet samples related to coronavirus.
| Extracted Tweet |
| Thank you corona to let us know what people are |
| شكرا كورونا ، كشفت معادن وايد من الناس |
| There are no corona cases today in jorden |
| و لله الحمد لم تسجل اي حالات اصابه بفيروس كورونا في الاردن |
Topic Modeling with BERT
BERT
This first pretext task objective of BERT is Mask Language Modeling (MLM). However, MLM is a token-level objective and
still, there is the need to learn sentences level representation. To learn these, a Next Sentence Prediction
(NSP) is proposed as the second objective to train BERT. However, the authors of RoBERTa
Arabic BERT
- 1.5 billion words Arabic Corpus
. - 3.5 million articles (∼1B tokens) from (OSIAN) the Open Source International Arabic News Corpus
. - Manually scraped Arabic news websites for articles.
The final size of the collected dataset afrer pre-processing is 70 million sentences, corresponding to ∼24GB of text.
BERTopic
Uniform Manifold Approximation and Projection for Dimension Reduction (UMAP)
Hierarchical Density-Based Spatial Clustering of Applications with Noise (HDBSCAN)
DBSCAN establishes a cluster using the minPoint as follows:
- (A) If there are four points near the core point we consider this point as core point.
- (B, C) If there is fewer than four points near the core point we consider this point as border point.
- (N) If there is no point near the core point, we consider this point as noise.
However, using \(\epsilon \) as a radius to cut the tree-like structure (dendrogram) point will result in lost points and noise, which leads to false clustering. HDBSCAN relies on a different approach by adding a parameter to control the cluster. This approach is more intuitive than clustering using the \(\epsilon \) because you never know how big the cluster needs to be.
Implementation
This blog post is inspired by the pilot study
Since the dataset is extracted from Twitter, we heavily pre-process the data to remove the tweets (1) that are not Arabic language, emoji and other non-ASCII characters. In addition, as we mentioned before, we normalize the tweets by removing diacritics (e.g., "ة", "ه").
For BERTopic we employ AraBERT(L) (Twitter version) which is trained on 60M Arabic dialects and tweets. The model uses the same tokenizer (word-piece tokenizer) as the original BERT model. The authors proposed another Sub-Word Units Segmentation method for Arabic. However, we will use the word-piece tokenizer-based model for the sake of comparability with the pilot study.
Result and Discussion
We compared the performance of different BERTopic based topic modeling techniques (LDA, HDBSCAN, and UMAP) on the Arabic tweets dataset. Table 3 shows the results of different BERTopic based topic modeling techniques and the improvement of using HDBSCAN and UMAP on the LDA model. Also, the combined model (HDBSCAN+UMAP) outperforms the other models.
Evaluation Metric. We use coherence metric \( C_{V} \)
| Model | \( C_{V} \) |
| LDA | 0.48896 |
| UMAP | 0.62195 |
| HDBSCAN | 0.63274 |
| UMAP+HDBSCAN | 0.63570 |
Table 4 shows the random topic extracted from the tweets dataset using BERTopic via UMAP. The first column shows the topic, and the second column shows the coherence score.
| Topic (AR/EN) | Score |
| عناصر member | 0.00573665129108314 |
| المتهم accused | 0.00552159281093779 |
| الشرطة police | 0.003955431150969441 |
| القضائية judgment | 0.0050212182104924 |
| اعتقال arrested | 0.00477325892023546 | المخدرات drug | 0.00416250245164534 |
Table 5 shows the most frequent topic extracted by HDBSCAN on the tweets dataset. The results represent the most frequent topics and trends in the Arab region tweets dataset (2020-2021).
| Count | Topics |
| 48138 | -1_ان_من_كورونا_الله (coronavirous) |
| 3365 | 0_عدن_اليمن_الانتقالي_الحوثي (Yeman war) |
| 3088 | 1_مش_ده_دي_ايه (trend or fahsion) |
| 2719 | 2_الدوري_الهلال_النصر_الاتحاد (saudi league) |
| 2019 | 3_الكويت_التعاونيه_الجمعيات_الحظر (charity ban) |
Also, we could visualize each topic using Wordcloud as shown in figure 4 below with topic=200.

Conclusion
In this short blog, we discuss Arabic language processing and how to apply BERTopic on the Arabic tweets dataset. We also present a comparison result between different models. Arabic tweets dataset is a good resource for Arabic NLP research. However, we believe that the Arabic tweets or short text dataset are not ideal for processing text to extract useful information (e.g., language modeling). The reason is that the tweets dataset is noisy and it is not representative of the Arabic language. For future work, we will use a larger Arabic dataset extracted from the wiki dump to fine-tined a better model. In addition, we plan to apply different families of language models such as GPT-2 and BART to the Arabic tweets dataset.
Extracting topic with GPT-4
GPT-4 is a new language model that is trained like ChatGPT on human feedback with a reward function to match the human intent or preferences.
Prompting is a technique that can be used to guide the model to generate a specific output. We can use the prompt to guide the model to generate a specific topic. For example, we can prompt the model to generate a topic about the COVID-19 pandemic. However, in this blog post we extract topics from the tweets dataset and therefore we want to employ the model to generate a topic from a given set of tweets. To do so, we can use the following prompt as a template :
To Guide the model: I have topic that contains the following documents:
Input Text
To Guide the model: Based on the information above, extract a short topic label in the following format:
Example of the desired output: topic:
This template will work with any language, next let's apply it to Arabic tweets.
I have topic that contains the following documents:
القحطاني كل عام نستعد لاستقبال شهر رمضان، ورمضان هذا العام هو رمضان الاسره ويجب علينا تطبيق قرارات الجهات المختصه، فرمضان هذا العام ياتي ونحن نواجه جاءحه كورونا ويجب تغير عاداتنا لتتوافق مع ما نمر به معا ضد الكورونا كلنا فريق البحر
Based on the information above, extract a short topic label in the following format:
topic:
topic: استعداد لشهر رمضان ومواجهة كورونا
A tweet about government coronavirus restrictions and Ramadan (fasting month). GPT-4 generated the exact topic: people's preparation for Ramadan.
I have topic that contains the following documents:
بريطانيا تتكفل بدفع من رواتب جميع موظفي القطاع الخاص محلات مطاعم شركات الخ الذين تضرروا بسبب ازمه كورونا شيء ممتاز يريدون الحفاظ علي هياكل الشركات وعدم انهيارها لكي تستانف اعمالها باي وقت ، و لمنع توجه من يفقد عمله نحو الجريمه
Based on the information above, extract a short topic label in the following format:
topic:
topic: بريطانيا تدعم رواتب الموظفين المتضررين من كورونا
Another correct topic generation by GPT-4 of a tweet about the coronavirus and the financial support from the government in the United Kingdom.
Also, we could use multiple documents:
I have topic that contains the following documents:
- صالونات التجميل والحلاقه عيادات البشره فتحت خلاص وصار قرار الذهاب راجع للشخص نفسه وكيف تعرفي انه الي يبيع في المطعم ولا في المول ولا حتي في السوبرماركت مافيه كورونا ؟ الموضوع راجع للحرص و لل
- بريطانيا تتكفل بدفع من رواتب جميع موظفي القطاع الخاص محلات مطاعم شركات الخ الذين تضرروا بسبب ازمه كورونا شيء ممتاز يريدون الحفاظ علي هياكل الشركات وعدم انهيارها لكي تستانف اعمالها باي وقت ، و لمنع توجه من يفقد عمله نحو الجريمه
- مقاطع متفرقه لحيوانات بدات تاخذ حريتها وتدخل المدن حول العالم بعد اختفاء البشر منها بسبب فايروس كورونا الذي الزمهم بالحجر المنزلي
- القحطاني كل عام نستعد لاستقبال شهر رمضان، ورمضان هذا العام هو رمضان الاسره ويجب علينا تطبيق قرارات الجهات المختصه، فرمضان هذا العام ياتي ونحن نواجه جاءحه كورونا ويجب تغير عاداتنا لتتوافق مع ما نمر به معا ضد الكورونا كلنا فريق البحر
Based on the information above, extract a short topic label in the following format:
topic:
topic: التأثيرات المختلفة لفيروس كورونا على المجتمع
Here, again but with multiple documents about coronavirus and its negative impact on society.
This also can work with indirect speech.
I have topic that contains the following documents:
احذر ان يستولي عليك الاحباط فتصبح صفرا في الحياه اصبر ، وقاوم ، وتحمل فالعثره التي تسقطك احيانا تنعشك ازمانا
Based on the information above, extract a short topic label in the following format:
topic:
topic: التغلب على الإحباط والصبر في الحياة
Also, GPT-4 can extract topics from indirect speech or wisdom, and in this example is a short wisdom about overcoming challenges in Life.
I have topic that contains the following documents:
السعداء اشخاص علموا ان الحزن ﻻ يجدد قديما، وﻻ يعيد ماضيا، وﻻ يرد غاءبا فتركوه جانبا، وابتسموا للحياه
Based on the information above, extract a short topic label in the following format:
topic:
topic: التفاؤل والابتسامة في مواجهة الحياة
Another example of indirect speech, this tweet is about being optimistic about life.